
Department of
Computational Perception

 |
Department of
Computational Perception
|
 |
MUSIC INTERFACES & VISUALIZATION
Automatic Playlist Generation and Personal Radio
Stations
| Consuming
music is most often a lean-back experience, requiring minimum (or
even no) interaction by the user. The aim is therefore simply that the
"right music" should be played back at
any time, preferrably in a meaningful sequence without explicit actions
and constant adjustment. In contrast to
traditional radio broadcasts that target a broad audience and a most
agreeable, generic music taste, such personalized radio stations
should address each user's individual need. Many factors
can play a role in what is considered the currently right music
including the user's general music
taste, the current emotional state, activity,
situation, surrounding, or social context. However, while implicilty
captured in listening histories of users to some extent, extracting
such factors remains the central challenge. Examples for projects:
Contact: Peter Knees, Markus Schedl |
 credit: Brian
Sawyer licensed under CC BY-SA 2.0 credit: Brian
Sawyer licensed under CC BY-SA 2.0 |
Intelligent Music Interfaces
| The general
philosophy is that music collections
should be structured (automatically, by the computer) and presented
according to intuitive musical criteria. Objectives are to develop
innovative, creative, appealing, user-centered, and playful
applications to access music and thus to enable new ways of discovering
hidden treasures in large
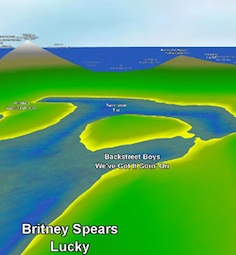
collections. One example is nepTune, an
interactive, landscape-like interface that permits and even encourages
the exploration of music
repositories. Examples for projects:
|
 |
Mobile Music Interfaces & Processing
| For
mobile devices the challenge is to provide powerful and efficient
algorithms and strategies to deal with the limited resources available
on such devices (e.g., processing power, screen resolution, interaction
capabilities). Music processing on such devices includes developing
optimized feature extractors and efficient usage of Web services.
Intelligent interfaces aim at elaborating novel and easy-to-use
paradigms to improve the user experience when sifting through music and
multimedia collections stored on the device or streamed from the Web. Examples for projects (can be carried out on Android and iOS platforms alike):
|
 |
Visualizations
| We
are also interested in and are actively developing various
visualization approaches for different application scenarios related to
information visualization and visual analytics.
Examples for projects:
|
 |
last edited by pk on Sep 29, 2015